
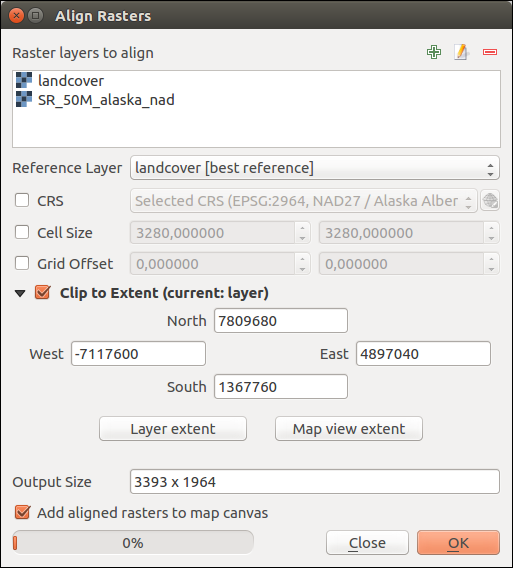
#Qgis define raster extent full
By completing this third class in the Specialization you will gain the skills needed to succeed in the full program. You should have equivalent experience to completing the first and second courses in this specialization, "Fundamentals of GIS" and "GIS Data Formats, Design, and Quality", before taking this course. Take Geospatial and Environmental Analysis as a standalone course or as part of the Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Specialization. This means that, unlike basic Cross-Tabulation, this analysis can only be.

#Qgis define raster extent how to
Learn how to visually display your data by classifying it in logical groupings and then symbolizing it on your map. raster format, where the spatial resolution is defined by the pixel size. Week 4: Expand your knowledge of symbology. Learn how to use environment variables to constrain your analyses and get better quality data products. Week 3: Go in-depth on projections and coordinate systems, which are foundational to all GIS. Take a detour into 3D data models, and interpolation of observations into 3D surfaces and rasters Week 2: Gain a working understanding of raster data models: symbolize, reproject, overlay, and assess rasters. Week 1: Tour ArcToolbox and learn how to use common geospatial analysis tools built into ArcGIS In this class you will learn the fundamentals of geospatial and environmental analysis during four week-long modules: Through all four weeks of this course, we'll work through a project together - something unique to this course - from project conception, through data retrieval, initial data management and processing, and finally to our analysis products. If you tick to show the clip Mask layer – SchoolPolygon – we can now see that our image was correctly clipped using the Mask layer.Apply your GIS knowledge in this course on geospatial analysis, focusing on analysis tools, 3D data, working with rasters, projections, and environment variables. Once you run this again, the output clipped raster tile, will have the areas outside the mask polygon changed to white, which now shows the clipped Raster tile as we would need it. This time, when you run the routine, tick the option to Create an output alpha band, in addition to the pre-ticked option to match the extent of the clipped raster to the extent of the mask layer. However the area around the edges of the tile, that fell outside of the Mask polygon are coloured as black pixels. Once ran it creates a new raster tile, showing only the area that falls inside the mask polygon. Then choose to output the result to a new File, saving the tile with a new name and choosing the image type e.g.tif
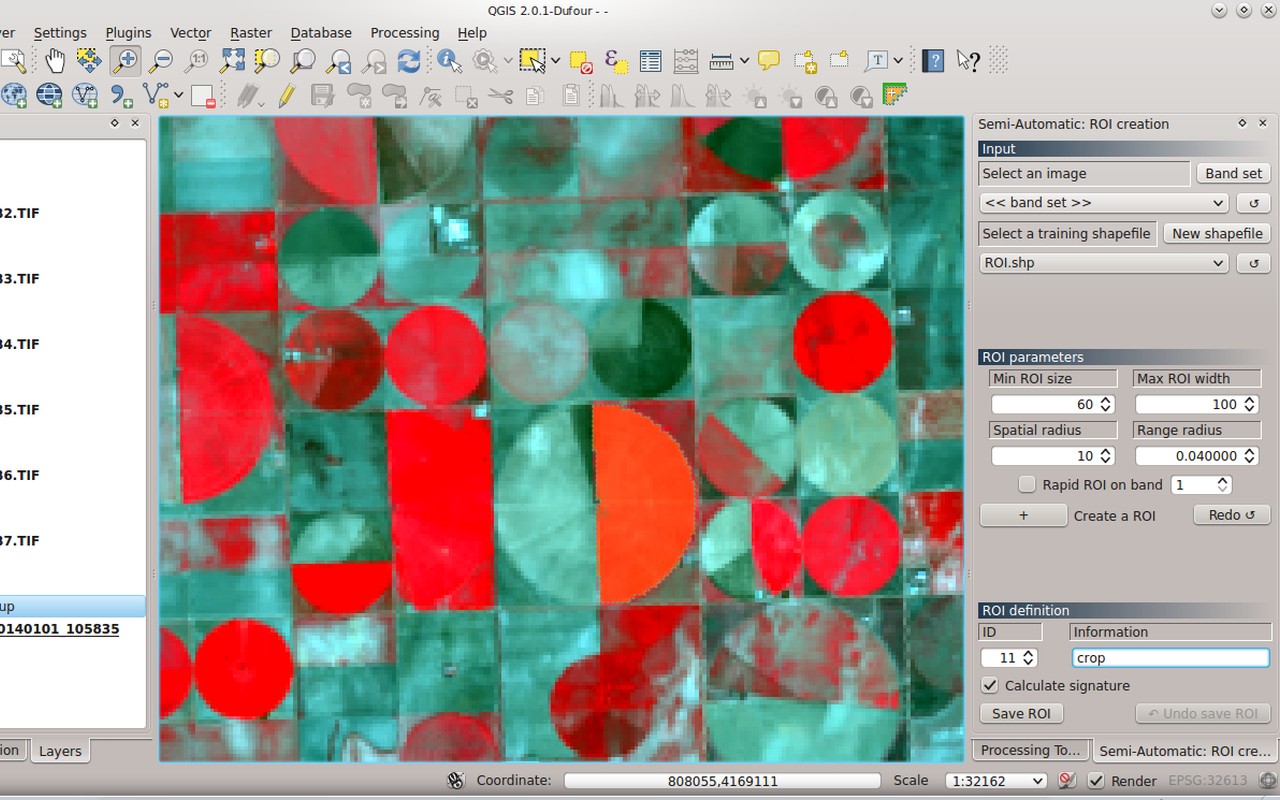
We will choose the second option, so from the menu Raster > Extraction > choose > Clip Raster by Mask Layer…Ĭhoose the input raster tile and the mask polygon layer, and set the Source CRS as needed – e.g. You can choose to clip the raster tile using the map extents, or by using a Mask Layer, such as the SchoolPolygon. Below we have one Raster tile – TQ0057 and a Mask Polygon called – SchoolPolygon.

However – you can also clip the Raster layer using the mask polygon to create a new tile that only includes the raster tile within the clip polygon area. The same idea can be applied with Raster tiles, where you could simply use the same vector inverted polygon to mask the raster layer that falls outside of the polygon – this could be useful for printing purposes. See this Cadline Community blog for more details: For example, using an inverted polygon boundary you can mask all layers that fall outside your area of interest – so that users only see the information that is important to them! Masks are commonly used to allow the end user to better interpret the map being shown to them. Is it possible to set a Mask around Raster Tiles in QGIS?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
